Industrial Automation is transforming manufacturing units in innumerable ways. It provides a conducive environment for machines and humans to work together in harmony for generating desired outcome. From improved operational efficiency, enhanced product quality, to trouble-free management of production processes, industrial automation has remarkably benefitted the manufacturing industry.
Automation in Manufacturing Industry
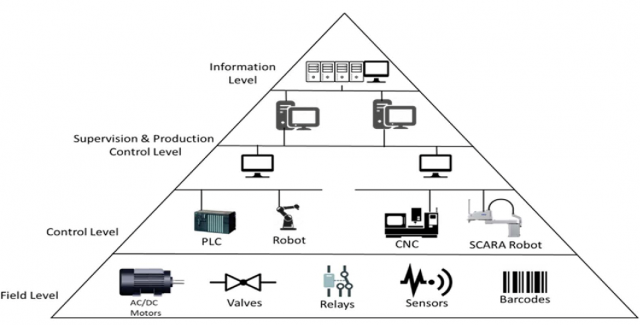
Automation in manufacturing refers to the use of modern technologies such as robots, computer software, PLCs, HMI systems, SCADA, etc. to manage equipment and processes within a factory. A logic controller is employed to manage the sequence of production, provide instructions, and handle the overall processes. Manufacturing operations such as production, material movements, administration of shop floor, assembly of products, packaging, etc. can be automated. It reduces human intervention and results in increased output, productivity, and accuracy.
How is Automation Transforming Manufacturing Operations?
With the advent of automation tools and technology, manufacturing industries have seen revolutionary changes. Plant equipment and system automation has minimized the need for manual operations and maximized performance. Further, it has improved the utilization of existing resources and enabled the ability to integrate innovative solutions for increasing manufacturing efficiency. Many industries have recognized and taken advantage of the potential benefits that industrial automation offers. All the processes right from planning, to execution, to delivery, each step can now be automated easily.
Let’s have a look at some prominent applications of automation in manufacturing operations and how businesses can leverage them to their advantage-
Automated Production Line:
An automated production line comprises a series of workstations linked by a conveyor system and an electrical control system. Each station executes a specific operation, and the product moves along the entire production line in a defined sequence.
How automated production line benefit manufacturers?
Automated Production Lines directly translate to less human intervention; hence the following benefits can be derived from it.
- Increased accuracy and quality of products.
- Increased efficiency of overall production unit.
- Swift and consistent production flow.
- Reduced production cycle time.
- Increased focus on system enhancement, planning, and supervision while machines do the job!
Various factories have leveraged the benefits of automated production lines and have achieved generated highest ROI. For instance: The production of a car in the automotive industry involves more than a hundred interconnected workstations where several parts are welded together, painted, assembled, checked for quality, and finally transform into a finished product. By deploying end-to-end automated lines dependency on human capabilities reduce, and factories can run 24×7 without interference of operators or shop-floor managers.
Use of Industrial Robots:
A wide array of applications ranging from pick and place, material handling, painting, mechanical cutting, plasma and gluing, assembly, inspection, machine tending, etc. can be performed using industrial robots. Almost any manufacturing operation can be performed with help of robots within a few minutes which might consume loads of time when performed manually.
How does the use of industrial robots benefit manufacturers?
Process automation with the use of industrial robots can ensure that production goals are met with minimum wasted efforts or expenses. Following are some of the most rewarding benefits of employing industrial robots-
- Robots help decrease cycle-time and cost-per-piece with enhanced operational efficiency.
- Robots can perform repetitive tasks persistently while maintaining precision levels of the products.
- Robots are designed to be hard-wearing and can operate in hazardous environments. Leading to improved safety of working professionals.
- Better floor space utilization can be achieved using robots.
- Increased production output.
Industrial robots have proved extremely advantageous for industries as they outperform human capabilities in terms of working efficiency. Humans have certain limitations and cannot work for longer hours, on the contrary robots can work non-stop for days or weeks. For instance: Robotic arc welding is one of the crucial processes for manufacturing ecosystems. The use of Robotic arc welders can improve the safety of workers by preventing inhalation of hazardous fumes and arc burns that might occur during the process. Moreover, it can perform high-quality welds in a limited cycle-time with exactness and closeness.
Predictive Maintenance:
Industrial systems and devices can develop failures at any point of time, and in turn, it may impact the production schedules. But, with industrial automation, manufacturers can now predict such failures in advance and prevent such occurrences that lead to downtime. Predictive maintenance uses real-time conditioning monitoring and analysis, to predict when and which equipment needs maintenance. It is more targeted and addresses a definite issue, unlike preventative maintenance that happens on scheduled cycles or after equipment breakdown.
How predictive maintenance can benefit manufacturers?
- Reduced cost of replacement since the issue is detected beforehand and necessary steps are taken before the damage occurs.
- Reduced machine-downtime.
- Enhanced equipment lifespan and efficiency.
- Improved production planning and scheduling, as operators are already aware of the maintenance hours.
Considering the above benefits, predictive maintenance will aid in operational efficiency and help save costs involved in maintenance.
Mobile Control of Automation Processes:
The use of Wi-Fi-connected tablets, smartphones, and mobile devices has enabled the ease of managing operations with no restrictions of presence. Integration of such devices supports shop floor managers and operators to remotely detect errors, control, and monitor production processes.
How mobile control of automation processes can benefit manufacturers?
- Enhanced supervision and monitoring of the overall process.
- Reduced labor costs as less manpower will be required to handle the process.
- Round-the-clock production with no need for the operator to be physically present.
- Easy access to information anytime and anywhere.
The importance of controlling automation processes remotely can be understood from the recent scenario of the pandemic. While the movement of people to the workplace was restricted and many industries were running at minimum efficiency, the use of remote access and monitoring of the production process has turned out to be convenient and extremely useful. It can empower industries to run at maximum efficiency even in the toughest times and under most challenging circumstances.
Challenges in Adoption of Automation
While automation has gained enormous traction, challenges in adoption persist for many industries. The biggest challenges that limit industries to fully embrace industrial automation include, resistance to process transformation, lack of expertise for strategic implementation and planning, training of shop floor operators, and inability to align goals with automation needs. Industries lack expert support who can understand the nature of their manufacturing processes and provide innovative automation solutions aligned to their requirements.
Solutions Provided by ENWPS
ENWPS is a group of highly skilled professionals who specialize in supply, installation, supervision, commissioning, and training services for industrial automation. We provide innovative automation solutions and strategies for process design and development, integration of automation systems, improvisation, and enhancement of existing processes, etc. to help industries stay competent in the global environment. For availing reliable and quality automation solutions, contact us at: rfq@enwps.com. And one of our team members will connect with you shortly!